Introduction to the Earth's Climate System

Kevin Trenberth
Former Coordinating Lead Author of the IPCC
The climate is a deciding factor in where to holiday, what food we eat and how we live. It guides animals in when to hibernate and when to mate. But what are the building blocks of our climate system and how does it work? Join pre-eminent climate scientist Kevin Trenberth as he guides us through the basics of the climate system.
The climate is a deciding factor in where to holiday, what food we eat and how we live. It guides animals in when to hibernate and when to mate. But what are the building blocks of our climate system and how does it work? Join pre-eminent climate scientist Kevin Trenberth as he guides us through the basics of the climate system.
Subscribe to watch
Access this and all of the content on our platform by signing up for a 7-day free trial.

Introduction to the Earth's Climate System
17 mins 5 secs
Key learning objectives:
Identify the five internal climate components
Understand how human activity has caused the climate crisis
Understand what the climate system is
Overview:
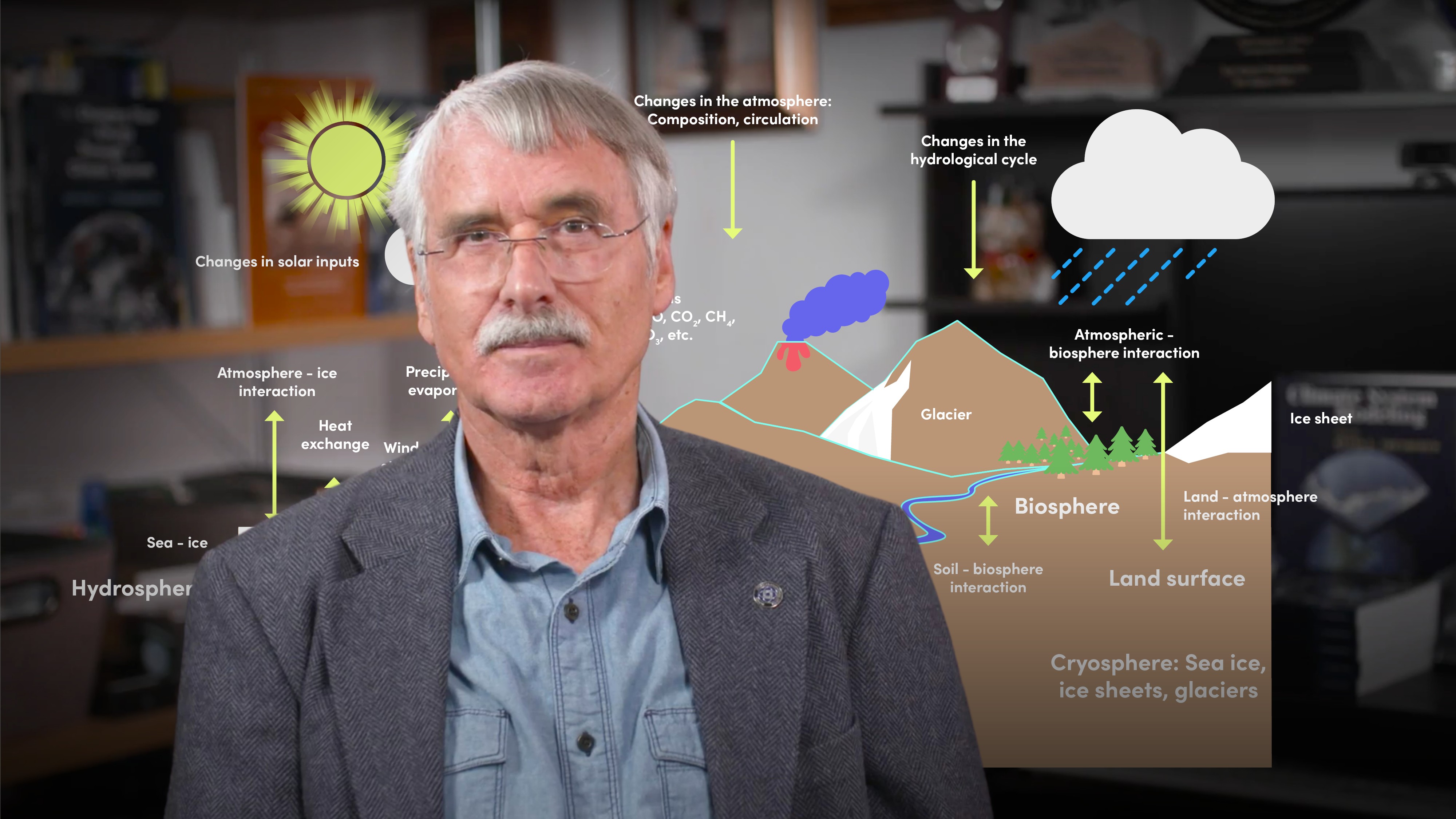
Our climate is a beautiful, interconnected and delicate balance of the Sun and our Earth. Put simply, the climate could be defined as: the average prevailing weather conditions in a region, including all the variability and extremes. It comprises five internal components (the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere) and the largest external component (the Sun). However, human activity has interrupted this delicate balance, causing our current climate crisis. The climate change we refer to and are living through, is a cause for alarm due to how rapidly the changes are occurring.
Subscribe to watch
Access this and all of the content on our platform by signing up for a 7-day free trial.
What is climate?
A succinct definition would be: the average prevailing weather conditions in a region, including all the variability and extremes.
What are the five major internal climate components?
1. Air (atmosphere). 99% of our atmosphere is made up of nitrogen and oxygen. Most of these contain two atoms, O2 and N2, that do not absorb radiation. As a rule of thumb, any gas with 3 or more atoms is a greenhouse gas and it absorbs radiation. Other important greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, water vapour, nitrous oxide and methane.
2. Water (hydrosphere). This includes all of the oceans, lakes and rivers. The circulation of the currents in the oceans move heat, salt, and chemicals.
3. Ice (cryosphere). This consists of the glaciers, permafrost and ice sheets, which are bright and reflect solar radiation.
4. Land surface (lithosphere). This refers to the mountains and land formations created from the Earth’s crust. These alter the disposition and movement of air.
5. Life (biosphere). This includes all living things on Earth, but perhaps most importantly, vegetation. Through photosynthesis, plants can absorb (take up) carbon dioxide, making rainforests extremely important to keeping our climate stable.
How does the Sun contribute to the climate?
Solar radiation is the energy that drives the climate. This electromagnetic radiation can be broken down into infrared radiation, radio waves, ultraviolet rays and visible light. Approximately 30% of all incoming electromagnetic radiation is reflected back by our atmosphere and the Earth's surface. 23% is absorbed by the atmosphere and 47% is absorbed by the Earth’s surface (land and oceans). Solar radiation is not spread equally across the planet. The equator gets the most, whereas the polar regions get very little. The differences in incoming radiation result in temperature differences that contribute to the weather, wind and ocean dynamics, as the winds and ocean currents carry warmth from the tropics to the poles.
How does human activity factor into the climate?
The climate change we refer to and are living through, is a cause for alarm due to how rapidly the changes are occurring.
Scientists agree that human activity is entirely responsible for the current climate crisis. Humans have been burning fossil fuels to keep our industry chugging along, flattening our forests for farming or urban use and increasing farming of livestock. All of this has contributed to greenhouse gas emissions and a buildup of greenhouse gas concentrations in our atmosphere.
Unlike water vapour, carbon dioxide has a long lifetime of centuries before it is taken out of the system. Accordingly, levels of carbon dioxide have risen by 48% since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution. Concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere is currently near 420 parts per million (or ppm) rising at around 2.5 ppm per year.
Subscribe to watch
Access this and all of the content on our platform by signing up for a 7-day free trial.

Kevin Trenberth
There are no available Videos from "Kevin Trenberth"