Introduction to Corporate Sustainability Reporting

David Wynn
15 years: Sustainability
Corporate sustainability reporting is a journey. Companies often focus on enhancing the coverage and quality of their data, setting targets, expanding the breadth of their reporting, and developing actions to improve performance after establishing a baseline. Join David as he explains us the meaning of sustainability data and and it's importance, through a corporate reporting lens.
Corporate sustainability reporting is a journey. Companies often focus on enhancing the coverage and quality of their data, setting targets, expanding the breadth of their reporting, and developing actions to improve performance after establishing a baseline. Join David as he explains us the meaning of sustainability data and and it's importance, through a corporate reporting lens.
Subscribe to watch
Access this and all of the content on our platform by signing up for a 7-day free trial.

Introduction to Corporate Sustainability Reporting
12 mins 53 secs
Key learning objectives:
Define what we mean by the term ‘sustainability’
What are the key data points that a company would need to understand to report on its sustainability
Tangible examples of environmental, social and governance (ESG) metrics
Understand why a company would be driven to report ESG data
Practical tips on where to start with reporting corporate sustainability data
Overview:
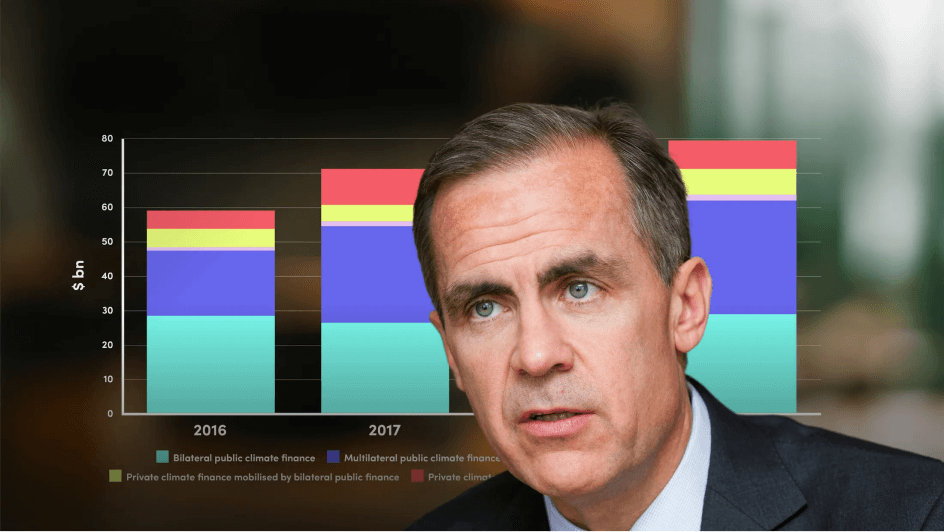
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the requirements for organizations to report on their sustainability data. Corporate reporting data in this space typically covers an organization’s environmental, social and governance impacts (or ESG). Understanding the importance of this data to different stakeholders and how to report it is an essential business practice.
Subscribe to watch
Access this and all of the content on our platform by signing up for a 7-day free trial.
What is sustainability data?
The term sustainability is used as an umbrella for multiple concepts and is today most commonly used as a synonym for being a ‘good’ company. When we apply an environmental lens, the definition is more focused on “the idea that goods and services should be produced in ways that do not use resources that cannot be replaced and that do not damage the environment”. Sustainability is commonly used today as a catch all term for how an organization applies its “do no harm” lens to how it operates.
What are ESG metrics?
Environmental, social and governance, or ESG, criteria have origins from the investment community, where investors use metrics on a company’s performance in each of these areas to assess the risks and opportunities within a company’s operations, and therefore their financial risk-return payoff.
- Environmental metrics consider how a company performs as a steward of the natural world.
- Social metrics examine how an organization manages relationships with employees, customers, suppliers and the communities in which it operates.
- Governance metrics look at a company’s leadership and how the organization is managed.
Why might a company report?
There are a number of reasons why a company might report their ESG metrics or sustainability information:
- Legal requirements
- Maintaining business
- Winning new business
- Understanding risks
- Positioning of products and services
- Staff, client and investor engagement and retention
How to start reporting sustainability data?
A company may use frameworks and standards to help them structure their corporate sustainability disclosures. Corporate sustainability reporting is a journey. Having established a baseline, companies will typically then focus on improving the coverage and quality of their data, setting targets, increasing the scope of their reporting and identifying initiatives to improve performance.
Subscribe to watch
Access this and all of the content on our platform by signing up for a 7-day free trial.

David Wynn
There are no available Videos from "David Wynn"